
Whats HOT
Latest Posts

Erasing History? Budget Cuts Threaten to Gut Ag History at Iowa State University
Author Michael Crichton noted, “If you don’t know history, then you don’t know anything. You are a leaf that doesn’t know it is part of a tree.” Opportunities to preserve Iowa’s ag history are being uprooted, however, as Iowa State University’s (ISU) College of Liberal Arts and Sciences (LAS) plans to make millions of dollars in budget cuts.
ISU’s history department is among the hardest-hit departments. The latest budget cut, when combined with an earlier cut, will reduce the history department’s budget by 34% during the next three years. To meet this target, the history department is considering eliminating its graduate programs and search for further economies.
“The decisions made today influence the future,” said Michael M. Belding III, 31, a Ph.D. candidate studying rural, agricultural, technological, and environmental history at ISU. “I disagree with the budget cuts for ISU’s history department, because the people of Iowa deserve better.”
Belding has been gathering signatures to challenge these budget cuts, which would eliminate graduate programs in ISU’s history department.

Michael M. Belding III, a Ph.D. candidate studying rural, agricultural, technological, and environmental history at Iowa State University (ISU), has been gathering signatures to challenge severe budget cuts that would eliminate graduate programs in ISU’s history department.
He took action after Dr. Beate Schmittmann, LAS dean, announced a new round of budget cuts as part of her “Reimagining LAS” initiative. This is intended to “right-size” the budget in response to changing enrollment and student demand and “to position the college for future success,” according to ISU.
Slashing the history department’s budget will destroy ISU’s nationally-recognized RATE program, which focuses on rural history, agricultural history, technology history and environmental history. “If these proposed budget cuts occur, ISU is throwing away an innovative, important program,” noted Dr. Pamela Riney-Kehrberg, a distinguished professor of history at ISU.
If this happens, there will be long-lasting, negative impacts for Iowa, added Dr. Joe Anderson, a professor of history at Mount Royal University in Calgary, Alberta. “The Midwest has long been dynamic powerhouse of agriculture and innovation,” said Anderson, who earned his Ph.D. in history at ISU. “Everyone who cares about Iowa and its past should be mad as hell about ISU’s decision.”
Iowa’s ag heritage isn’t just for history majors
The risk of losing graduate programs in ISU’s history department doesn’t just affect future historians or professors. “This will limit opportunities to preserve Iowa’s cultural heritage,” said Dr. Kevin Mason, an assistant professor of history at Waldorf University in Forest City.
Not everyone who enrolls in history classes at ISU is a history major, added Mason, who received his Ph.D. in rural and environmental history from ISU in 2020. They include attorneys, engineers, architects and high school teachers who want to expand their knowledge of Iowa’s heritage. “If you care about Iowa history, you need to understand ag history.”
The only other university offering anything similar to ISU’s RATE program is Mississippi State University (MSU), although MSU focuses on Southern—not Midwestern—history. Neither the University of Iowa nor the University of Northern Iowa focus on ag/rural history, Riney-Kehrberg added.
“In most history courses and books, there’s little or no information on ag history following the Civil War,” noted Riney-Kehrberg, who researches American rural and agricultural history and will soon publish her latest book, When a Dream Dies: Agriculture, Iowa and the Farm Crisis of the 1980s. “The standard American history textbook might have one sentence about the Farm Crisis.”
The same dearth of information is evident when it comes to the role of women in agriculture. “There are many women’s studies courses today, but they often only teach the story of urban women, not rural women,” Riney-Kehrberg added.

“If these proposed budget cuts occur, ISU is throwing away an innovative, important program,” notes Dr. Pamela Riney-Kehrberg, a distinguished professor of history at Iowa State University.
History comes to life through the “land-grant land hunt”
While Yale University offers agrarian studies, it’s not the boots-on-the-ground style of research and extension that a land-grant university like ISU provides, Riney-Kehrberg noted.
Brandon Duxbury experienced this first-hand through the “land-grant land hunt” that ISU Extension undertook from 2014-2018. Contrary to popular belief, not a single acre of Story County land was given to Iowa State as part of the land-grant act (the Morrill Act) of 1862. Iowa was the first state to accept the provisions of the Morrill Act to build a college for the study of agriculture and the mechanical arts. Iowa Governor Samuel Kirkwood appointed Peter Melendy to select the best 210,000 acres of Iowa land to fund the new land-grant college. Most of this land was available in north-central and northwest Iowa.
Iowa became the first state to digitally map all these land-grant parcels within the state. Duxbury, a South Dakota native and graduate student in ISU’s history program, researched countless historical documents and interviewed current landowners to share their stories of their farmland. “People were always excited when we contacted them about this project,” said Duxbury, who is the new curator of collections at the Dacotah Prairie Museum in Aberdeen, South Dakota.
These stories, videos, a digital map and more can be found at www.landgrant.iastate.edu. “Efforts like this inspire people to ask better questions about the legacy they’re leaving with the land,” Duxbury said.
Making Iowa history relevant in ways like this is vital, said Belding, a Story City native who has links to his petitions on his Twitter account @mickey_belding. “I grew up thinking history involved big events that happened elsewhere, not here in Iowa. The more I research Iowa’s ag history, though, the more attached I get to Iowa.”
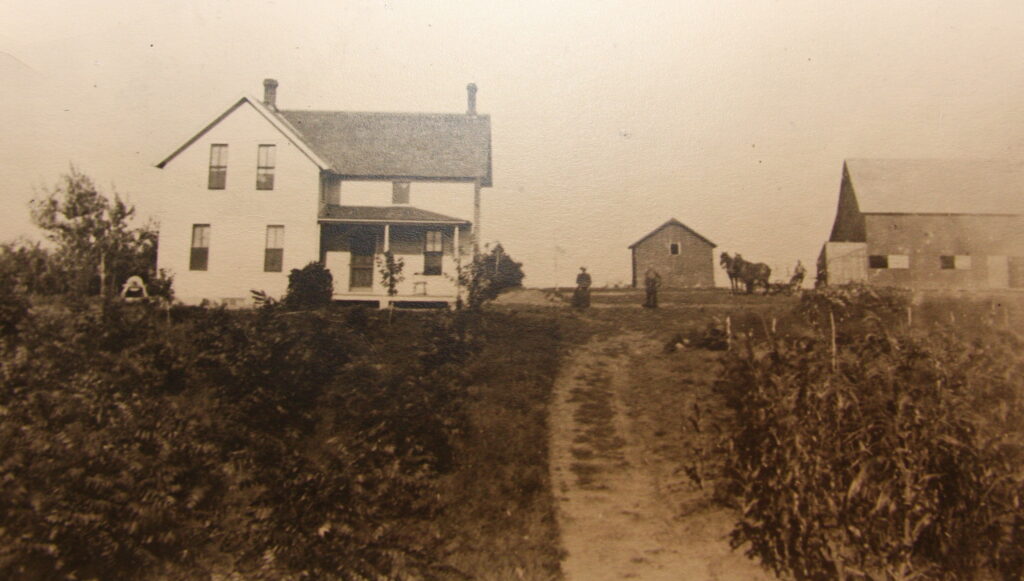

Family farms like this one near Yetter in Calhoun County have driven the economy in Iowa and the Midwest for generations. “The Midwest has long been dynamic powerhouse of agriculture and innovation,” says Dr. Joe Anderson, a professor of history at Mount Royal University in Calgary, Alberta, who earned his Ph.D. in history at Iowa State University (ISU). “Everyone who cares about Iowa and its past should be mad as hell about ISU’s decision.”
Teaching history prepares students for success
Along with researching and preserving Iowa history, ISU’s history department helps students develop a broad skill set, including communication. “My dad was a computer programmer who was promoted to management,” Riney-Kehrberg said. “He always emphasized that reading, writing and speaking skills were essential for a successful career.”
History classes also teach students research skills, data analysis and critical thinking. “You have to make an argument, and then find facts to support this argument,” Riney-Kehrberg said. “All this requires you to think carefully and broadly.”
Studies show that students with a solid LAS education, including history, have some of the best outcomes five years after college graduation. “These graduates tend to make more money, are the least likely to be fired, are less likely to move back home to live with their parents and are more likely to be promoted,” said Anderson, citing sources like the 2018 report “Humans Wanted: The Coming Skills Revolution,” published by the Royal Bank of Canada. “We’re very short-sighted as a culture if we devalue skills that come from studying the humanities.”
The “soft skills” of how people communicate with each other, interact with colleagues and solve problems are just as important to workplace readiness and employability as hard skills, especially as technology evolves. “It doesn’t take a ‘George Jetson’ moment to imagine a day when artificial intelligence and other technologies will replace some of the jobs we currently train people for,” Anderson, who served as director of history and interpretation at Living History Farms in Urbandale in the 1990s. “Our society will always need people who are skilled in human connection and communication.”
Society also needs educated citizens, both rural and urban, with a solid understanding of agricultural history, Anderson added. “People who are trained in ISU’s history department often go on to run museums in Iowa and the Midwest, teach at community colleges like DMACC or Hawkeye Community College, teach at land-grant universities, or pursue a variety of other careers.”
Everywhere they go, these professionals take Iowa history with them, noted Anderson, a south-central Nebraska native who loved spending time on his grandparents’ farms in Missouri and Iowa. He often incorporates Midwestern history into the classes he teaches in Canada. “This perspective helps people better understand many pressing issues today, from water quality to food production.”
Integrating history with tourism, economic development
It’s essential to be open to new ways of making Iowa history relevant to a wider audience, Mason said. “I believe history departments, especially at a land-grant like ISU, can collaborate across academic disciplines to help create a more diversified economy that encourages young people to stay in Iowa.”
Mason, who grew up in Pella, saw how Iowa history was intertwined with job creation, economic development and tourism in his hometown. “Tradition is important in Pella. Honoring this heritage helps young people gain a sense of place and the sense of pride that comes from knowing their history.”
Anyone who is concerned about the proposed funding cuts to ISU’s history department should contact their state legislators, the Board of Regents, and Dr. Beate Schmittmann, dean of the College of LAS at ISU. It’s important to take action now, Duxbury said. “The loss of ISU’s graduate history programs is a loss to Iowa history. Fighting these drastic cuts is a battle worth fighting.”
Note: I wrote this article for Farm News. It first appeared in the Friday, May 27, 2022, edition of Farm News. I’ve had a number of people ask me what they can do to fight these budget cuts. First, if you’re an Iowan, contact the senator and representative who represent you at the state level in the Iowa legislature. Also, contact leaders at ISU, including:
Iowa State University
Attn. Dr. Beate Schmittmann
202 Catt
2224 Osborn Dr.
Ames IA 50011-4009
Iowa State University
Office of the President, Dr. Wendy Wintersteen
515 Morrill Road
1750 Beardshear Hall
Ames, IA 50011
Want more?
I invite you to read more of my blog posts if you value intriguing Iowa stories and history, along with Iowa food, agriculture updates, recipes and tips to make you a better communicator.
If you’re hungry for more stories of Iowa history, check out my top-selling “Culinary History of Iowa: Sweet Corn, Pork Tenderloins, Maid-Rites and More” book from The History Press. Also take a look at my other books, including “Iowa Agriculture: A History of Farming, Family and Food” from The History Press, “Madison County,” “Dallas County” and “Calhoun County” book from Arcadia Publishing. All are filled with vintage photos and compelling stories that showcase the history of small-town and rural Iowa. Click here to order your signed copies today! Iowa postcards are available in my online store, too.
If you like what you see and want to be notified when I post new stories, be sure to click on the “subscribe to blog updates/newsletter” button at the top of this page, or click here. Feel free to share this with friends and colleagues who might be interested, too.
Also, if you or someone you know could use my writing services (I’m not only Iowa’s storyteller, but a professionally-trained journalist with 20 years of experience), let’s talk. I work with businesses and organizations within Iowa and across the country to unleash the power of great storytelling to define their brand and connect with their audience through clear, compelling blog posts, articles, news releases, feature stories, newsletter articles, social media, video scripts, and photography. Learn more at www.darcymaulsby.com, or e-mail me at yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Let’s stay in touch. I’m at darcy@darcymaulsby.com, and yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Talk to you soon!
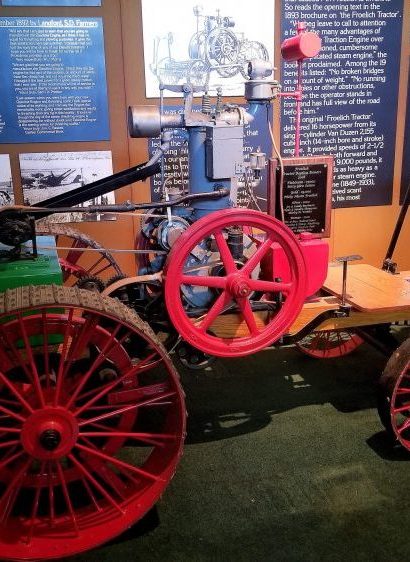

Machines that Changed America: John Froelich Invents the First Tractor in Iowa
Today, it’s hard to imagine a cornfield without a tractor in the picture. I was thinking about tractor history when The History Channel featured “The Machines That Built America.” I was glad to see they included the story of John Froelich, which I featured in my 2020 book Iowa Agriculture: A History of Farming, Family and Food.
Here’s an excerpt:
Back in 1892 in the tiny village of Froelich in Clayton County, Iowa, however, folks were amused by what a local businessman, John Froelich, was saying.
This northeast Iowa entrepreneur (1849 -1933) believed that mechanical power had a great future—that someday traction engines would do the work of horses even on mid-sized and large farms. The locals had to admit, though, that Froelich had invented several handy gadgets, including a more efficient washing machine, plus he was a good businessman.
Froelich ran a grain elevator, plus he ran a well-digging business and operated a threshing rig. Every year he took a crew of men to Langford, South Dakota, to work the fields. Froelich had considerable experience with steam engines and knew their pitfalls. They were heavy and bulky. They were hard to maneuver. They were always threatening to set fire to the grain and stubble fields. On the flat prairie, with a strong wind blowing, that was no joke.
A frustrated Froelich decided he could invent a better way to power the engine. The solution was gasoline. Froelich and local blacksmith Will Mann came up a vertical, one-cylinder engine mounted on the running gear of a steam traction engine – a hybrid of their own making. They designed many new parts to make it all fit together, but it finally was done. The word “tractor” wasn’t used in those days, but that’s what Froelich invented.
A few weeks later Froelich and his crew started for the broad fields of South Dakota with the “tractor” and a new threshing machine. That fall they threshed 72,000 bushels of small grain. It was a success!
Later that fall, Froelich shipped his “tractor” to Waterloo, Iowa, to show some businessmen. Immediately, the men formed a company to manufacture the “Froelich Tractor.” They named the company The Waterloo Gasoline Traction Engine Company and made Froelich the president.
Unfortunately, efforts to sell the practical, gasoline-powered tractor failed. Two were sold and shortly returned. The company then decided to manufacture stationary gas engines to provide income while tractor experiments continued, according to the Froelich Museum.
In 1895, the Waterloo Gasoline Engine Company was incorporated, but Froelich, whose interest was in tractors, not stationary engines, chose to withdraw from the company. The Waterloo Company continued to build stationary engines while trying to improve the tractor. In 1913 the model “L-A” was made.
In 1914, the first Waterloo Boy tractor, the Model “R” single-speed tractor, was introduced. Farmers liked it, and sales reached 118 within a year. When the Model “N” Waterloo Boy with two forward speeds was introduced, it was also successful.
When World War I led to rising farm prices and strong demand for dependable mechanical farm power, the concept of the tractor became so popular many tractor manufacturers sprung up in a matter of months. Deere and Company in Moline, Illinois, which manufactured a full line of John Deere implements, had been watching the progress of the Waterloo Engine Company and the increasing quality of its products.
Deere was looking for an established farm tractor to round out its line, and the Waterloo Engine Company fit the bill. Today, Deere’s facility in Waterloo remains one of the largest tractor-producing plants in the nation.
Tractors of various types and sizes that make farming easier and more efficient are shipped to farmers all over the world. For this contribution, John Froelich will long be remembered, and the village of Froelich, Iowa, remains “Tractor Town U.S.A.”
Tractor enthusiasts from around the globe travel to this tiny village to visit the birthplace of the tractor. At the 1891 general store, guests can view a scale model of the first “Froelich Tractor” made from the original blueprints. Perhaps the monument erected in 1939 near the general store best captures the essence of this unique place.
“In this village, John Froelich built the first gasoline tractor that propelled itself backwards as well as forward. Far-reaching in its effect on modern agricultural history, it moved out of this village and into the world in 1892. Later that year, Mr. Froelich joined with others in organizing the Waterloo Gasoline Traction Engine Company, which later became the John Deere Tractor Company.”
Meeting the challenge of a reliable, durable tractor
This history took center stage at the 2018 Iowa State Fair in Des Moines, when a butter sculpture of the Waterloo Boy Tractor stood next to the world-famous Butter Cow in the John Deere Agriculture Building’s 40-degree cooler throughout the fair, which ran from August 9-19.
To understand the significance of the Waterloo Boy, take a trip back in time, said Neil Dahlstrom, manager of the John Deere Archives and History. In the critical five-year stretch (1912-1917) prior to John Deere entering the tractor business, there were two key issues to address.
“First, what did farmers really want from a machine that would soon make the horse obsolete?” said Dahlstrom, who noted that salesmen, territory and branch managers, and Deere’s top leadership scoured the country to understand what customers desired. Also, how could the equipment to be manufactured to be durable enough to stand up to daily farm use?
Deere had considered every imaginable idea. The company had developed one-, two- and four-cylinder concept tractors. Some ran on gasoline. Others ran on kerosene. Some had all-wheel drive. Others had front-wheel drive. The company even explored concepts like line steering, which was meant to replicate horse reins as the steering mechanism to ease farmers into power farming, Dahlstrom said.
A motorized cultivator, what Deere called a “Tractivator,” was brought to market by several competitors, but Deere determined it did not provide any cost savings compared to horses.
The challenge of producing a durable tractor loomed large. In a letter to company president William Butterworth in 1915, Deere’s superintendent of factories George Mixter noted that tractors offered by competitors up to that point “have not been built with the proper spirit behind the design and manufacture to insure their durability in the hands of the farmers.” But if Deere could “build a small tractor that will really stand up for five or more years’ work on the farm, I believe they will be a permanent requirement of the American farmer,” Mixter wrote.
Deere ultimately found the solution with the Waterloo Boy tractor and acquired the Waterloo Gasoline Engine Company in Waterloo, Iowa, on March 14, 1918. Although anxious to start selling the Waterloo Boy, Deere dealers had to wait while Deere honored existing contracts, which did not expire until Dec. 31, 1918, Dahlstrom said.
Waterloo Boy makes its debut
Deere put its money where its instincts were. Over the next year, the company spent more than one-third of its advertising budget touting the Waterloo Boy tractor, Dahlstrom said.
Specifically, Deere invested $50,000 on tractor advertising in the year following its debut of the Waterloo Boy—approximately $747,000 in today’s money. Another way to get the company’s new product out in front of customers was to take it on the road – literally.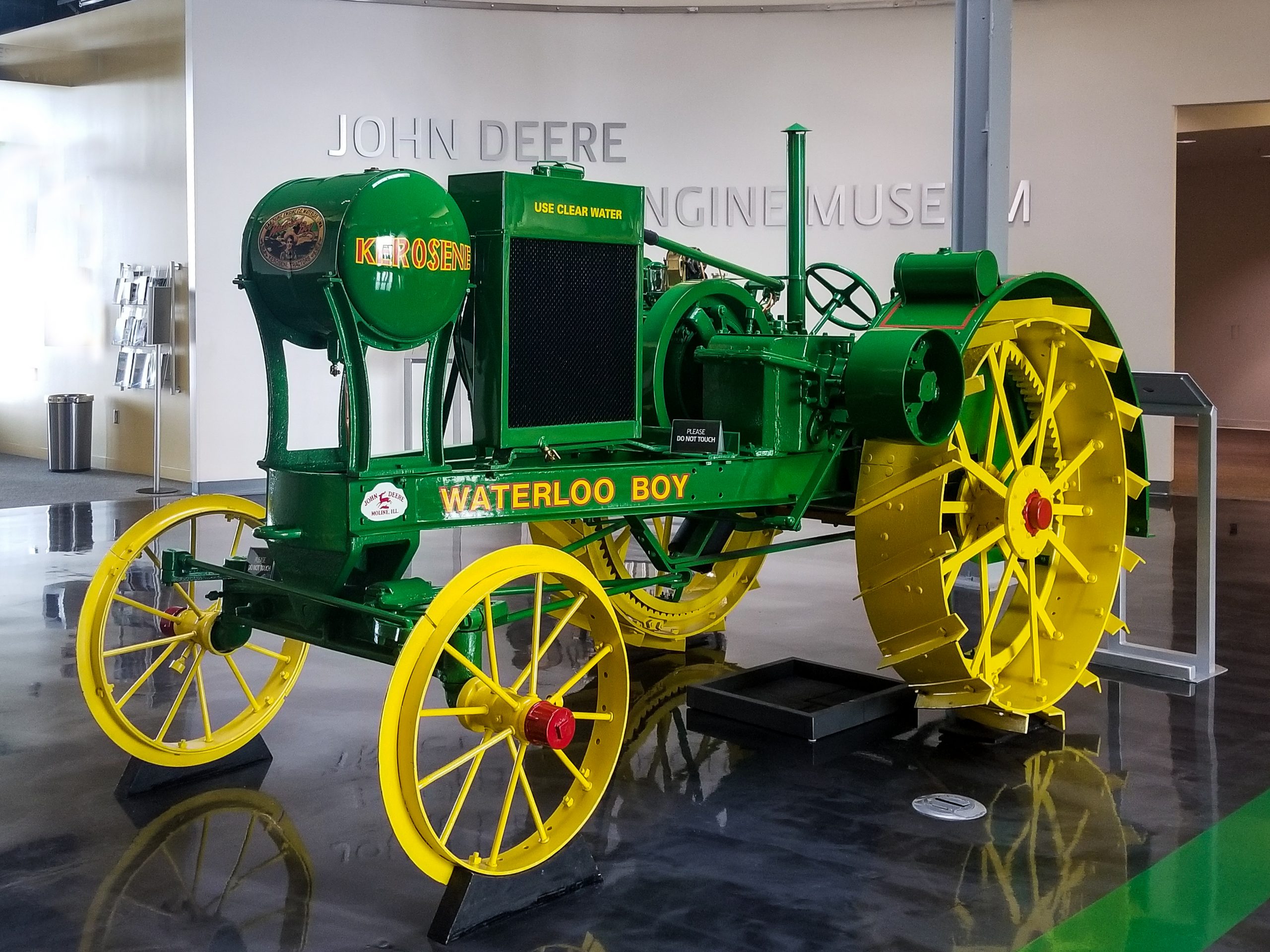 The National Tractor Demonstrations started to become more mainstream after being introduced in the United States in 1913. An eight-city, eight-week tour schedule was the perfect opportunity to unveil Deere’s Waterloo Boy, Dahlstrom said. Salina, Kansas, served as the ideal backdrop in August 1918, since this was the nation’s largest demonstration.
The National Tractor Demonstrations started to become more mainstream after being introduced in the United States in 1913. An eight-city, eight-week tour schedule was the perfect opportunity to unveil Deere’s Waterloo Boy, Dahlstrom said. Salina, Kansas, served as the ideal backdrop in August 1918, since this was the nation’s largest demonstration.
Deere had participated in tractor demonstrations since the original Winnipeg Agricultural Motor Competitions in Manitoba, Canada, in 1908 – but not with a tractor. Instead, Deere had paired its plows with leading tractor manufacturers. That changed now that the Waterloo Boy was part of the Deere family.
At Salina, Deere spared no expense, showcasing 12 Waterloo Boy tractors as the centerpiece of a display that included John Deere signs, Waterloo Boy signs and a copper leaping deer statue, Dahlstrom said. “There were two stars during this week of 100-degree days – ‘ice water on tap’ and the Waterloo Boy Model ‘N’ tractor,” he added.
The Model “N” demonstrated its merits by pulling tractor plows, disc harrows and grain drills. Visitors were shuttled in three John Deere farm wagons pulled by Waterloo Boy tractors. By all accounts, the debut was a success.
“The award for the most elaborate, largest and most artistic exhibit tent at the Salina tractor show will undoubtedly go to the John Deere Plow company of Kansas City,” wrote the editors of a Kansas City newspaper.
As Deere’s advertising campaign swung into full gear, the Waterloo Boy tractor was promoted as the “best and most efficient tractor” on the market for farmers inclined to buy a tractor. By October 1918, readers of Deere’s magazine, The Furrow, saw an advertisement for the line of Waterloo Boy tractors and stationary engines. The ad guaranteed the Waterloo Boy’s “ample power for field and belt work.”
In January 1919, with tractors now available through John Deere dealers, Deere’s first print ad for the trade press appeared in The Farm Implement News. It featured two areas of emphasis: “A Good Tractor Backed by a Permanent Organization.”
After years of development, John Deere customers and John Deere dealers finally had their John Deere tractor. “It took longer than the company expected, but a determination to do it right instead of doing it fast now brought the John Deere tractor to market,” Dahlstrom said.
As a result, customers got “the assurance of more tractor work per dollar of fuel cost; longer tractor life with less repair cost; accessibility of parts that makes caring for the tractor simple and easy; and dependable power for all farm work.”
The tractor era had officially arrived, and Iowa found itself at the epicenter of this growing industry.
Want more?
I invite you to read more of my blog posts if you value intriguing Iowa stories and history, along with Iowa food, agriculture updates, recipes and tips to make you a better communicator.
If you’re hungry for more stories of Iowa history, check out my top-selling “Culinary History of Iowa: Sweet Corn, Pork Tenderloins, Maid-Rites and More” book from The History Press. Also take a look at my other books, including “Iowa Agriculture: A History of Farming, Family and Food” from The History Press, “Madison County,” “Dallas County” and “Calhoun County” book from Arcadia Publishing. All are filled with vintage photos and compelling stories that showcase the history of small-town and rural Iowa. Click here to order your signed copies today! Iowa postcards are available in my online store, too.
If you like what you see and want to be notified when I post new stories, be sure to click on the “subscribe to blog updates/newsletter” button at the top of this page, or click here. Feel free to share this with friends and colleagues who might be interested, too.
Also, if you or someone you know could use my writing services (I’m not only Iowa’s storyteller, but a professionally-trained journalist with 20 years of experience), let’s talk. I work with businesses and organizations within Iowa and across the country to unleash the power of great storytelling to define their brand and connect with their audience through clear, compelling blog posts, articles, news releases, feature stories, newsletter articles, social media, video scripts, and photography. Learn more at www.darcymaulsby.com, or e-mail me at yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Let’s stay in touch. I’m at darcy@darcymaulsby.com, and yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Talk to you soon!

Bob Feller on Farming, Baseball and Military Service
Now that we’re in the time of the year when we take time to honor those who’ve served (Memorial Day), celebrate America (July 4) and maybe even catch a baseball game, I think about the time I interviewed Bob Feller, a Major League Baseball legend and Iowa farm kid.
I’m willing to bet that most people, if they are old enough to remember Feller, know him more for his pitching prowess with the Cleveland Indians. But Feller was also a decorated World War II veteran who gave up some of his prime years of playing professional baseball to serve his country.
“I’m very proud of our military and have a lot of respect for our troops,” said Feller (1918-2010) when I interviewed him in his hometown of Van Meter, Iowa, in 2003.
Known as the “Heater from Van Meter,” Feller signed a pro baseball contract with the Cleveland Indians when he was only 16. “Farm work made me a ball player,” Feller said. “When I was little, I was the water boy for the threshing crew. As I got older, I did it all—I cleaned the barn, milked cows, drove tractors and teams of horses, picked corn and threw bales of hay. Those bales really helped strengthen my arms.”
Feller’s father, Bill, was his first coach. “When I was a kid, Dad built a ball field we called Oak View. That was the first Field of Dreams—not that one from the movies.”
Feller grew up playing baseball at vacation Bible school at the Methodist Church in Van Meter. He also played four years of American Legion baseball in Adel, where his catcher was Nile Kinnick, a future University of Iowa football star who would enlist in the Navy Air Corps Reserve three days after the attacks on Pearl Harbor.
Feller’s father spent hours helping his son develop his baseball skills. “Dad would hit ground balls to me in the hog lot and pitch batting practice to me. We’d practice every night we could. When Mom would call us for supper, we’d always tell her we could eat after dark, but we couldn’t play ball after dark.”
“I never thought twice about enlisting”
By the time Feller played his first game in the major leagues in 1936, the teenaged pitcher struck out 15 St. Louis Browns. Later that season, at age 17, Feller set a new American League record by fanning (striking out) 17 Philadelphia Athletics. In Chicago in 1940, Feller pitched his first of three no-hitters and the only no-hitter pitched on opening day in major league history.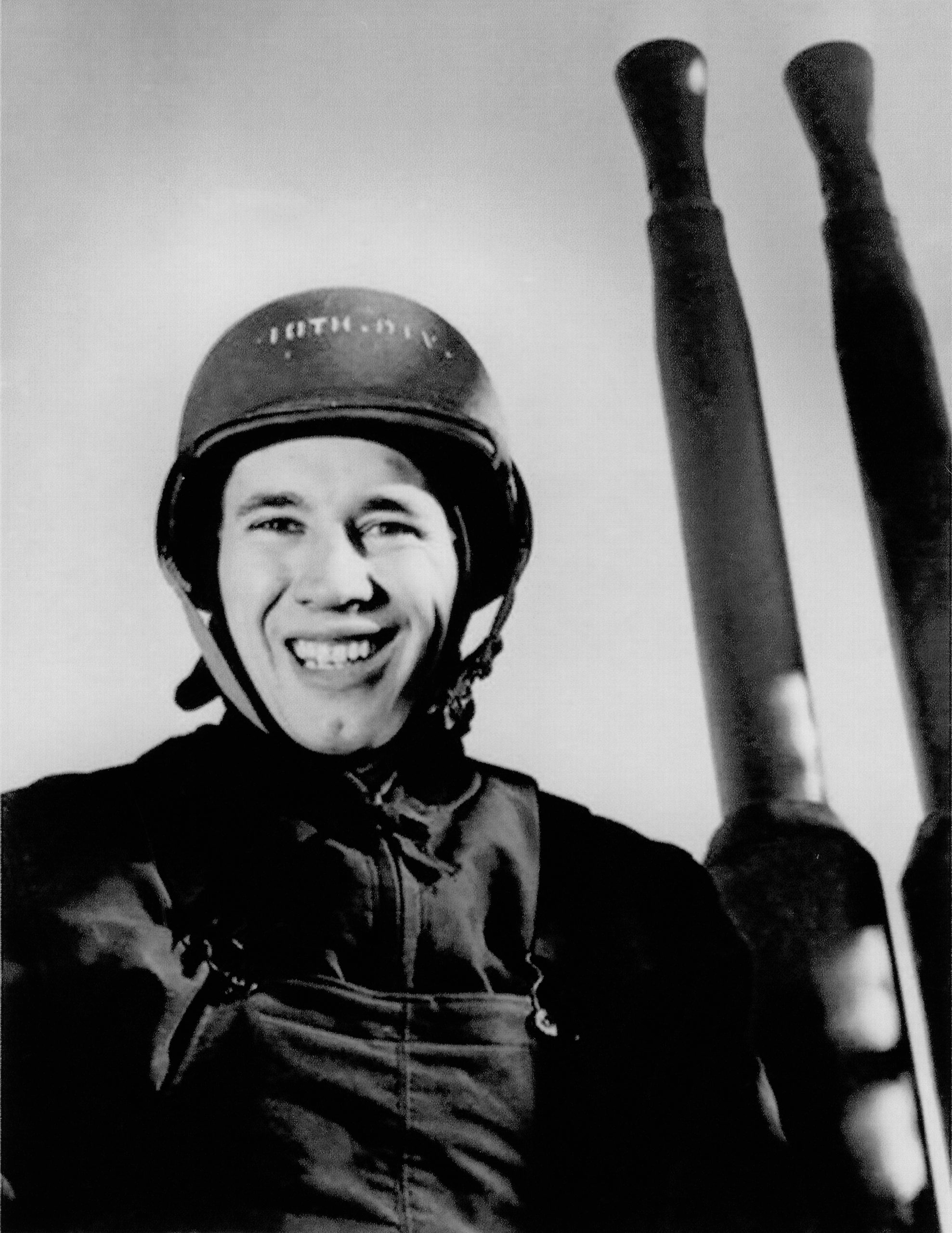 On the eve of World War II, Feller was playing in the big leagues with stars like Ted Williams and Joe DiMaggio. By the time Feller enlisted in the Navy two days after the Pearl Harbor attacks on December 7, 1941, the 22-year-old star had already set a number of major league records.
On the eve of World War II, Feller was playing in the big leagues with stars like Ted Williams and Joe DiMaggio. By the time Feller enlisted in the Navy two days after the Pearl Harbor attacks on December 7, 1941, the 22-year-old star had already set a number of major league records.
While some say Feller’s military service took away what could have been some of his most productive years, Feller doesn’t see it that way.
“I never thought twice about enlisting. I played a little baseball during boot camp in Norfolk, Virginia, before I became an anti-aircraft gun captain on the USS Alabama for 34 months.”
Feller was awarded eight Battle Stars during his years of service. When the war ended, Feller resumed his baseball career with the Cleveland Indians in the late summer of 1945. “I’m no hero,” emphasized Feller, who was inducted into the Hall of Fame in 1962, after retiring from baseball in 1956 at age 37. “I’m just a survivor. The men who never returned home to this country were the heroes.”
Maybe Feller’s story resonates me so much because I, too, come from rural Iowa, and I’ve been blessed to know many friends and family members who have served our country. America is home to a significant percentage of veterans. In 2011–2015, nearly one fourth (24.1 percent) of the veteran population 18 years and older lived in areas designated as rural, according to census.gov.
While we don’t know them all, we owe them all. Thanks to you all, and thanks to patriots like Bob Feller who was willing to serve when his country needed him. America truly is the home of the free because of the brave.
Want more?
I invite you to read more of my blog posts if you value intriguing Iowa stories and history, along with Iowa food, agriculture updates, recipes and tips to make you a better communicator.
I’ve shared more Bob Feller stories and photos in my Iowa history book “Dallas County.”
If you’re hungry for more stories of Iowa history, check out my top-selling “Culinary History of Iowa: Sweet Corn, Pork Tenderloins, Maid-Rites and More” book from The History Press. Also take a look at my other books, including “Iowa Agriculture: A History of Farming, Family and Food” from The History Press, “Madison County,” “Dallas County” and “Calhoun County” book from Arcadia Publishing. All are filled with vintage photos and compelling stories that showcase the history of small-town and rural Iowa. Click here to order your signed copies today! Iowa postcards are available in my online store, too.
If you like what you see and want to be notified when I post new stories, be sure to click on the “subscribe to blog updates/newsletter” button at the top of this page, or click here. Feel free to share this with friends and colleagues who might be interested, too.
Also, if you or someone you know could use my writing services (I’m not only Iowa’s storyteller, but a professionally-trained journalist with 20 years of experience), let’s talk. I work with businesses and organizations within Iowa and across the country to unleash the power of great storytelling to define their brand and connect with their audience through clear, compelling blog posts, articles, news releases, feature stories, newsletter articles, social media, video scripts, and photography. Learn more at www.darcymaulsby.com, or e-mail me at yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Let’s stay in touch. I’m at darcy@darcymaulsby.com, and yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Talk to you soon!
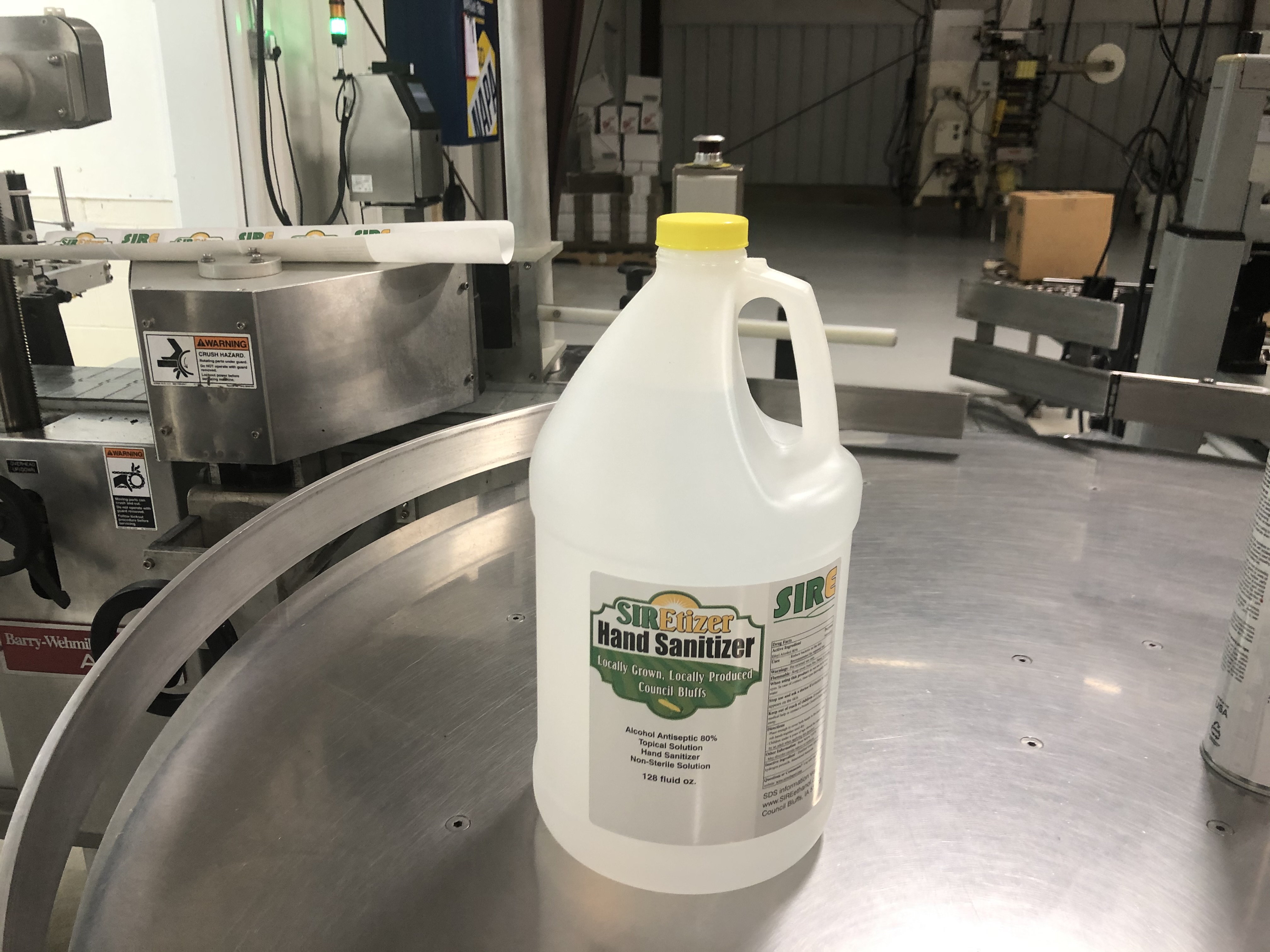

Sauce to Sanitizer: Cookies Food Products Bottles Hand Sanitizer Made with Ethanol
Going with the flow takes on a whole new meaning in times like this COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic. It also explains why ethanol-based hand sanitizer has been flowing through the bottling line instead of barbecue sauce at Cookies Food Products Inc. in Wall Lake, Iowa.
“I’m a firm believer you have to pay rent for the space you occupy while you’re here on earth,” said Speed Herrig, who has grown Cookies Food Products into one of the largest regional sauce manufacturers in the country in the past 40 years. “We want to do what we can to help.”
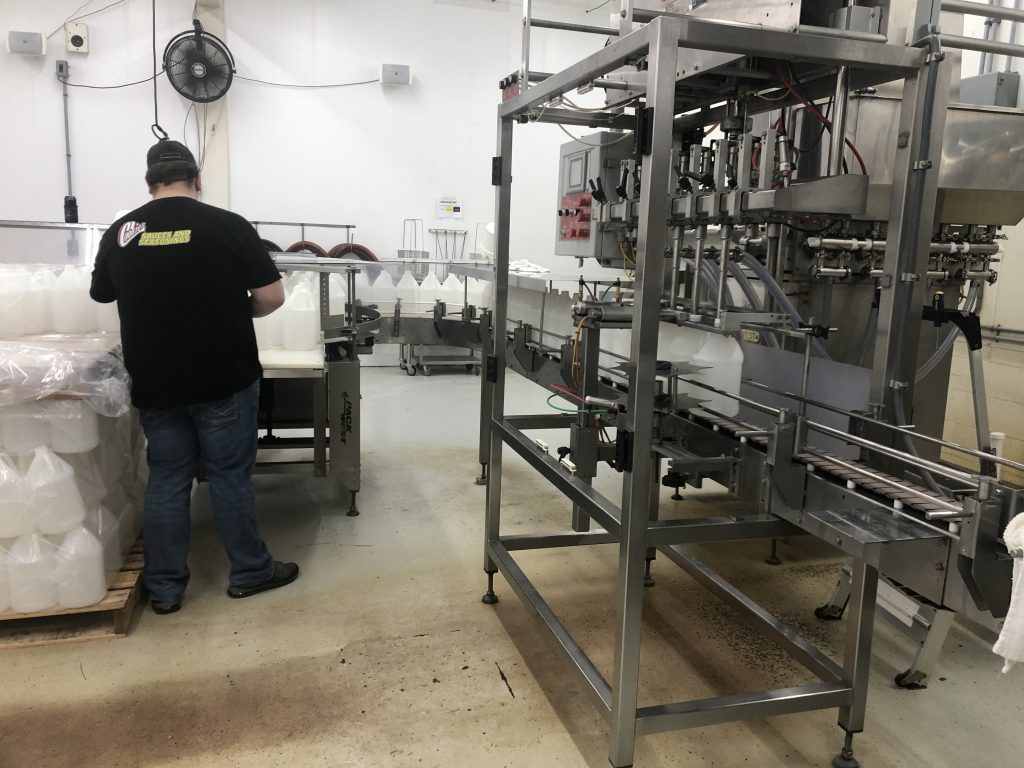
That’s why Herrig didn’t hesitate to offer his company’s bottling resources when he heard that Southwest Iowa Renewable Energy (SIRE) near Council Bluffs was trying to fill bottles by hand with ethanol-based hand sanitizer they’d produced. Filling bottles manually from large plastic totes was complicated and slow, especially when time is of the essence to help protect people’s health.
Herrig knew there was a better way. Just as General Motors retooled some of its production lines to make ventilators during the COVID-19 pandemic, Cookies made some small modifications on its equipment so employees could fill jugs with hand sanitizer instead of barbecue sauce. The Cookies team filled 5,000 1-gallon jugs with hand sanitizer in a couple days in mid-April for SIRE. “We’re fortunate to have a lot of long-term, experienced employees at Cookies, so it wasn’t too hard to make these changes,” Herrig said.
 Corn-based solutions fuel innovation
Corn-based solutions fuel innovation
By early April, hospitals and nursing homes in Iowa and beyond were desperately searching for hand sanitizer, as demand for the product soared. Ethanol plants that can make large batches of sanitizer’s main ingredient, alcohol, offered to help.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has stringent production standards designed to protect the quality of medicines, food ingredients and dietary supplements. Previously, the agency prohibited many ethanol plants from using their alcohol that didn’t meet high quality specifications for use in drugs or beverages.
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, however, FDA revised its regulations, noted Justin Schultz, SIRE regulatory manager, who was quoted in the Council Bluffs Nonpareil newspaper several weeks ago. With the FDA’s new guidelines, ethanol made at plants that produce fuel ethanol can be used in a product like hand sanitizer, if the ethanol contains no additional additives or chemicals. Ethanol plants must also ensure water purity and proper sanitation of equipment.
SIRE produces more than 130 million gallons of fuel-grade ethanol per year and consumes more than 44.6 million bushels of corn annually. After FDA revised its guidelines this spring, SIRE shipped a few hundred gallons of pre-mixed hand sanitizer to Cookies’ Wall Lake bottling facility in early April. Once the Cookies team readjusted some settings to ensure the sanitizer would flow through their bottling system properly, they began filling 5,000 1-gallon plastic jugs.
The jugs of hand sanitizer were shipped to the Des Moines area to increase the state’s stockpile for distribution throughout Iowa. Herrig is glad that more people will be able to get the hand sanitizer they need, without being at the mercy of con artists.
“I’ve seen scammers selling hand sanitizer for well over twice the price it should be,” Herrig said. “Changing $75 a gallon or $10 for an 8-ounce bottle is outrageous. I don’t want to see anyone price gouging.”

Giving back
While Herrig added that the Cookies team played a small role in the fight against COVID-19, they viewed this as a way to help their fellow Iowans in a time of need.
“We’ve enjoyed doing business in Iowa for many years through our sauce business, our automotive parts business and our golf cart business,” said Herrig, who opened an automotive parts and repair business in 1962 on his family’s farm near Wall Lake. “Iowa has been a good place for me, and I want to give back.”
This article first appeared in the April 24, 2020, issue of Farm News.
Want more?
I invite you to read more of my blog posts if you value intriguing Iowa stories and history, along with Iowa food, agriculture updates, recipes and tips to make you a better communicator.
If you’re hungry for more stories of Iowa history, check out my top-selling “Culinary History of Iowa: Sweet Corn, Pork Tenderloins, Maid-Rites and More” book from The History Press. Also take a look at my other books, including “Iowa Agriculture: A History of Farming, Family and Food” from The History Press, “Dallas County” and “Calhoun County” book from Arcadia Publishing. All are filled with vintage photos and compelling stories that showcase the history of small-town and rural Iowa. Click here to order your signed copies today! Iowa postcards are available in my online store, too.
If you like what you see and want to be notified when I post new stories, be sure to click on the “subscribe to blog updates/newsletter” button at the top of this page, or click here. Feel free to share this with friends and colleagues who might be interested, too.
Also, if you or someone you know could use my writing services (I’m not only Iowa’s storyteller, but a professionally-trained journalist with 20 years of experience), let’s talk. I work with businesses and organizations within Iowa and across the country to unleash the power of great storytelling to define their brand and connect with their audience through clear, compelling blog posts, articles, news releases, feature stories, newsletter articles, social media, video scripts, and photography. Learn more at www.darcymaulsby.com, or e-mail me at yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Let’s stay in touch. I’m at darcy@darcymaulsby.com, and yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Talk to you soon!
Darcy

The Corn Lady: Jessie Field Shambaugh and the Birth of 4-H in Iowa
Well-behaved women rarely make history. At a time when young girls in rural Iowa generally weren’t encouraged to broaden their knowledge of agriculture, Jessie (Field) Shambaugh chose to attend educational farm meetings with her father by the time she was 12 years old. She went on to become one of the first female ag teachers in the nation. By the time she was 24, she was elected superintendent of schools for Page County, Iowa. “The Corn Lady,” as she was affectionately known, also helped guide the formation of an innovative new learning opportunity that endures today–4-H–with the goal to “make the best better.”
Farm women have long broken new ground in rural Iowa. Jessie Field Shambaugh (sister of the famous nursery and garden innovator Henry Field) guided the formation of today’s 4-H clubs during her tenure as a country schoolteacher in southwest Iowa.
Born in 1881 on a farm near Shenandoah, Shambaugh started her career teaching taught country school in southwest Iowa. By the turn of the twentieth century, “Miss Jessie” was a woman far ahead of her time. An innovative teacher, she introduced basic science classes in addition to the “3 Rs” in the country school curriculum. She believed in teaching country children in terms of country life and was a strong proponent of relating school lessons more closely to life on the farm and in the rural home.

Jessie Field Shambaugh of Iowa
By developing the Boys’ Corn Club and the Girls’ Home Club, Miss Jessie created the forerunner of 4-H and became the first female ag teacher in the nation. Her knowledge of agriculture was extensive, as her father had encouraged her to learn about farming methods from the time she was a young girl. As early as age twelve, Miss Jessie attended local Farmers’ Institute meetings with her father and listened to presentations from ag leaders like “Uncle Henry” Wallace, who edited Wallaces’ Farmer.
Inspired by these ideas, Miss Jessie promoted hands-on, practical learning. She pioneered a powerful educational concept to help young people learn “to make the best better.” By age twenty-four, Miss Jessie had been elected superintendent of schools for Page County. She was one of the first female county superintendents in Iowa.
Starting in 1906, she enlisted the assistance of the 130 one-room country schools in the county to form boys’ and girls’ clubs. Miss Jessie encouraged the young people to participate in judging contests. She believed that friendly competition inspired students to excel. At the Junior Exhibits held at the Farmers’ Institute in Clarinda, entry classes for students included “Best 10 Ears of Yellow Dent Corn,” “Best Device Made by a Boy for Use on the Farm” and “Best 10 Ears of Seed Corn Selected by a Girl.”
Miss Jessie’s efforts gained national attention from educators and reporters. She hosted the U.S. Commissioner of Education and state superintendents as they toured Page County clubs in 1909. She designed the 3-leaf clover pin to reward 3-H project winners and wrote the Country Girls Creed. Jessie Field Shambaugh’s vision and pioneer spirit led to 4-H clubs nationwide, notes the Iowa 4-H Foundation.

4H logo
The goal was to “make the country life as rewarding as it might be in any other walk of life,” Miss Jessie noted in The Very Beginnings. While she passed away at age 90 in 1971, Shambaugh was inducted into the Iowa Women’s Hall of Fame in 1977, and her legacy lives on.
“My mother always wanted to help the farm boys and girls,” said Miss Jessie’s daughter, Ruth Watkins of Clarinda, whom I interviewed in 2002. “She had great idealism and was able to carry it through to reality.”
This is the spirit that inspired me to post this on March 8–International Women’s Day (IWD). I’ve long been inspired by rural Iowa women like Miss Jessie, who were breaking new ground as they became a force for good in their local community, long before the first IWD, which dates back to 1911. I think Miss Jessie would agree with the IWD’s philosophy that “We are all parts of a whole. Our individual actions, conversations, behaviors and mindsets can have an impact on our larger society.”
Want more?
Thanks for stopping by. Miss Jessie’s story is just one of the remarkable women featured in Chapter 9, “Iowa Women Blaze New Trails in Agriculture,” in my upcoming book Iowa Agriculture: A History of Farming, Family and Food, which will be release on April 27, 2020, by The History Press.
In the meantime, I invite you to read more of my blog posts if you value intriguing Iowa stories and history, along with Iowa food, agriculture updates, recipes and tips to make you a better
If you’re hungry for more stories of Iowa history, check out my top-selling “Culinary History of Iowa: Sweet Corn, Pork Tenderloins, Maid-Rites and More” book from The History Press. Also take a look at my latest book, “Dallas County,” and my “Calhoun County” book from Arcadia Publishing. Both are filled with vintage photos and compelling stories that showcase he history of small-town and rural Iowa. Order your signed copies today! Iowa postcards are available in my online store, too.
If you like what you see and want to be notified when I post new stories, be sure to click on the “subscribe to blog updates/newsletter” button at the top of this page, or click here. Feel free to share this with friends and colleagues who might be interested, too.
Also, if you or someone you know could use my writing services (I’m not only Iowa’s storyteller, but a professionally-trained journalist with 20 years of experience), let’s talk. I work with businesses and organizations within Iowa and across the country to unleash the power of great storytelling to define their brand and connect with their audience through clear, compelling blog posts, articles, news releases, feature stories, newsletter articles, social media, video scripts, and photography. Learn more at www.darcymaulsby.com, or e-mail me at yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Let’s stay in touch. I’m at darcy@darcymaulsby.com, and yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Talk to you soon!
Darcy

When Agriculture Entered the Long Depression in the Early 1920s
The culture of Iowa agriculture hasn’t only been shaped by good times. The farm crisis that started in the 1920s, a decade before the Great Depression engulfed America, shook rural Iowa to its core. In the post–World War I era, the Golden Age of Agriculture was over, and farmers throughout the Midwest began to suffer the effects of an increasing economic depression that culminated at the close of the 1920s with the stock market crash.
“To understand the nature of the agricultural problem more clearly, it needs to be said that farming is a difficult and uncertain profession,” noted Gary D. Dixon in his thesis “Harrison County, Iowa: Aspects of Life from 1920 to 1930,” which he presented in 1997 to the Department of History to earn his Master of Arts degree from the University of Nebraska–Omaha. “The farmer has no control over the prices he pays for goods or, more importantly, for what he can ask for his own products, as he ‘buys in a seller’s market, and he sells in a buyer’s market.”

Wesells Living History Farm WW1
It was definitely a seller’s market during World War I, when all sectors of the American economy produced as much as possible to help the war effort. It was profitable, as well as patriotic, to raise crops at top capacity. But then the war ended on November 11, 1918.
“Government price supports for agriculture were kept through 1920, when the guaranteed prices on wheat and other crops were terminated,” Dixon noted. “The government ended loans to European nations at the same time, which meant they were unable to purchase U.S. agricultural products.”
This is what had kept the exports going, and exports had driven the boom in the U.S. farm economy. In the years just after World War I, prices for farm goods fell by half, as did farmer income. The Federal Reserve raised the credit rate just when the farmer needed its help the most, so money tightened up. Banks did not renew notes, but mortgages and bills still came due. To make it worse, the railroads raised their freight rates, so it was more expensive to get the crops to market, Dixon noted.
Farm income fell from $17.7 billion in 1919 to $10.5 million in 1921—nearly a 41 percent drop. In Iowa, farm values that had almost tripled between 1910 and 1920 plunged during the 1920s. In Harrison County in southwest Iowa, 1930 land values of $41 million reflected a drop of more than $35 million from 1920, Dixon said. In addition, Harrison County’s total crop values, which in 1919 were more than $10.8 million, fell to roughly $5.7 million by 1924. “Taxes on the remaining income, and the other expenses incurred in farming, remained as high as they ever were, or increased,” Dixon added.
While there had been a historic growth in the number and size of farms in the nation until 1920, that soon changed. Then the farm population showed net losses of 478,000 in 1922 and 234,000 in 1923. The more lucrative prospects of the city lured many of the best of the younger generations away, Dixon said.
Iowa farm, 1920s Source: Library of Congress
Banding Together in Farmer Cooperatives
In response to these troubling developments, some farmers began organizing with their neighbors so their shared concerns could be heard at the county, state and national level. Some turned to groups like the Iowa Farmers Union, which had formed in 1915 to help members work together to strengthen the independent family farm through education, legislation and cooperation.
Others turned to a new group, the Iowa Farm Bureau Federation (IFBF), which had formed on December 27, 1918, during a meeting in Marshalltown. The sSeventy-two county Farm Bureau groups from across Iowa voted unanimously during this meeting to form a state federation. These farmers knew that they needed a stronger voice in legislation governing their industry, improved marketing for their ag products and better relationships with other related industries, including meatpackers and the railroads.
“We regard this movement as one of the most sensible efforts toward an organization of farmers that has yet been made,” said Henry A. Wallace, the editor of Wallaces’ Farmer, who went on to become U.S. secretary of agriculture and vice president of the United States.
The IFBF also helped support the cooperative marketing movement that had been gaining momentum, noted Tim Neiss, IFBF historian. Ag cooperatives had started to form in Iowa by the mid-1800s in response to unfair business practices by the railroads that hurt competition and lowered the prices farmers received for their products. Farmers began banding together to market their products more efficiently, at higher prices, as well as to buy inputs at lower cost.
One of these early Iowa cooperatives was Farmers Cooperative Elevator of Marcus, which was incorporated on December 12, 1887. The Marcus location, which is now part of First Cooperative Association based in Cherokee, remains the oldest active cooperative elevator in the nation.
While organizing into farm organizations and cooperatives appealed to some farmers, other farmers decided to move in a much more radical direction—one of that would culminate in the Farmers Holiday movement and the near-lynching of an Iowa judge in Le Mars. Get the whole story in my book Iowa Agriculture: A History of Farming, Family and Food, which is published by The History Press the week of April 27, 2020.
Want more?
Thanks for stopping by. I invite you to read more of my blog posts if you value intriguing Iowa stories and history, along with Iowa food, agriculture updates, recipes and tips to make you a better
If you’re hungry for more stories of Iowa history, check out my top-selling “Culinary History of Iowa: Sweet Corn, Pork Tenderloins, Maid-Rites and More” book from The History Press. Also take a look at my latest book, “Dallas County,” and my “Calhoun County” book from Arcadia Publishing. Both are filled with vintage photos and compelling stories that showcase he history of small-town and rural Iowa. Order your signed copies today! Iowa postcards are available in my online store, too.
If you like what you see and want to be notified when I post new stories, be sure to click on the “subscribe to blog updates/newsletter” button at the top of this page, or click here. Feel free to share this with friends and colleagues who might be interested, too.
Also, if you or someone you know could use my writing services (I’m not only Iowa’s storyteller, but a professionally-trained journalist with 20 years of experience), let’s talk. I work with businesses and organizations within Iowa and across the country to unleash the power of great storytelling to define their brand and connect with their audience through clear, compelling blog posts, articles, news releases, feature stories, newsletter articles, social media, video scripts, and photography. Learn more at www.darcymaulsby.com, or e-mail me at yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Let’s stay in touch. I’m at darcy@darcymaulsby.com, and yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Talk to you soon!
Darcy

Memories of Carroll County, Iowa, Century Farm Endure
Among the most remarkable parts of rural Iowa are the thousands of families who have owned the same land for 100 years. I’ve had the chance to interview hundreds of Iowa families who own Century Farms. Some of these folks, like Bill Bruggeman, share the kinds of stories you never forget.
After Bill passed away this week (read his touching obituary here), I felt that sharing his story would be a fitting tribute to a dedicated, kind, hard-working Iowa farmer I respect greatly Here’s his story, which I wrote in 2017 for Farm News:
While all the buildings that once graced the Bruggeman family’s Carroll County Century Farm between Lidderdale and Lake City are gone, the memories live on.
“The times keep changing,” said Bill Bruggeman, 85, who lives with his wife, Doris, on a farm a few miles northeast of his family’s Sheridan Township Century Farm. “This spring I saw a farmer on RFD TV who could plant 2,500 acres a day. This country is going big.”
It’s a big switch from the 120-acre Carroll County farm that Bruggeman’s grandfather, John Bruggeman, purchased in 1903. John and his wife, Emma, had farmed near Johnson, Nebraska, before deciding their farming prospects were brighter back in Iowa.
While Bruggeman didn’t grow up on the Century Farm where his grandparents lived, he has fond memories of the farmstead, which once boasted a large farmhouse and barn. “When I was a little kid I’d go across the fields on Saturday mornings to get Grandma Emma’s fresh-baked cinnamon rolls,” he recalled.
Good food was perk of farm life, which was often filled with long days of hard work and few luxuries. “We didn’t get electricity on the farm until the 1940s and didn’t get running water until the 1950s,” Bruggeman said.
Horsepower sometimes came from the family’s Farmall tractor, but it also came in the form of May and Babe. “I loved that team,” said Bruggeman, whose family used the horses to plant corn, pull the manure spreader and haul hay. “They didn’t run away.”
Those were the days when 12 neighborhood families worked together in a threshing ring, a tradition that lasted until the mid-1950s. While Bruggeman’s father, Carl, and the other men worked in the field, Bruggeman’s mother, Marie, prepared fried chicken, roast beef, mashed potatoes, fruit pies, cream pies and more to serve the hungry men at noon.
“Around 5 p.m. you’d haul the last load of the day,” said Bruggeman, who noted that the wives provided the threshing crew with snacks around 3 p.m. “The men were usually served supper, too.”
The day’s work wasn’t done, however, since each farmer had chores to do at home. “Back then, many farms had about 20 beef cows, some dairy cows and about 10 sows,” Bruggeman said.

While the demands of farm work limited trips to town, there was fun to be had when it to was time to buy groceries. Bruggeman enjoyed the outdoor movies shown in Lidderdale in the summer months, back when the town had three grocery stories and about as many gas stations. “Dad would give me a nickel so I could get a pop or popcorn,” said Bruggeman, who recalled how cars were lined up on both sides of the town’s busy business district.
Money was hard to come by in those days, and crop yields were nowhere close to what farmers produce today. “When I was a kid, 60 bushels per acre of corn was a really good yield,” said Bill Bruggeman, who started farming full-time in 1955 after completing his military service. As improved corn hybrids become available, Bruggeman won the DEKALB Yieldmasters Club award in 1976 for producing 113.39 bushels of corn per acre.
While much has changed in agriculture since the Bruggemans were raising their four children (including Sheila, Brenda, Cathy and Brett) on the farm, the family is proud to honor the legacy of their Century Farm, which is now owned by Brett Bruggeman.
“It’s wonderful to have a Century Farm,” said Bruggeman, who retired from farming three years ago. “We’re lucky to have one.”
Bruggeman Carroll County Century Farm
• Established: 1903
• Township: Sheridan
• Acres: 120
• Century Farm Award given in 2016
• 4th generation farm
Want more?
Thanks for stopping by. I invite you to read more of my blog posts if you value intriguing Iowa stories and history, along with Iowa food, agriculture updates, recipes and tips to make you a better
If you’re hungry for more stories of Iowa history, check out my top-selling “Culinary History of Iowa: Sweet Corn, Pork Tenderloins, Maid-Rites and More” book from The History Press. Also take a look at my latest book, “Dallas County,” and my “Calhoun County” book from Arcadia Publishing. Both are filled with vintage photos and compelling stories that showcase he history of small-town and rural Iowa. Order your signed copies today! Iowa postcards are available in my online store, too.
If you like what you see and want to be notified when I post new stories, be sure to click on the “subscribe to blog updates/newsletter” button at the top of this page, or click here. Feel free to share this with friends and colleagues who might be interested, too.
Also, if you or someone you know could use my writing services (I’m not only Iowa’s storyteller, but a professionally-trained journalist with 20 years of experience), let’s talk. I work with businesses and organizations within Iowa and across the country to unleash the power of great storytelling to define their brand and connect with their audience through clear, compelling blog posts, articles, news releases, feature stories, newsletter articles, social media, video scripts, and photography. Learn more at www.darcymaulsby.com, or e-mail me at yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Let’s stay in touch. I’m at darcy@darcymaulsby.com, and yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Talk to you soon!
Darcy

What’s the Scoop? Expanded Wells’ Ice Cream Parlor Offers a Taste of Iowa
Love ice cream? Think you can handle something as outrageous as the Monster Peanut Butter Cup Sundae? Then you MUST visit Le Mars, Iowa, soon. Everything is bigger and better at the revamped Wells Visitors Center and Ice Cream Parlor in downtown Le Mars, from the extreme milkshakes and sundaes (Savannah Peach, anyone?) to the spacious parlor itself, where you
can enjoy their sweet treats in the retro-styled dining area or new movie theater upstairs.
“This is a one-of-a-kind experience,” said Adam Baumgartner, vice president of retail sales for Wells Enterprises, Inc., whom I visited with during a recent media day at the ice cream parlor. “Beyond the Iowa State Fair, we want to make this the single-biggest tourist attraction in Iowa.”
More than 200,000 people have visited the parlor each year since it opened in 2011. “Our goal is to more than double that,” said Baumgartner, who noted that the remodeled parlor/visitor center blends education, entertainment and unique experiences for guests of all ages.
In the past year, Wells has invested $3 million in upgrades and expansions for the rebranded facility, which is housed in a historic 1917 building on Central Avenue. Highlights include:
• An interactive “farm to spoon” look at ice cream, from the dairy farm to the grocery store.
• An expanded ice cream menu with more novelties, extreme shakes and desserts, including the Lemon Meringue Shake, Monster Peanut Butter Cup Sundae, Molten Chocolate Lava Shake and more.
• An ice cream cone-shaped display where guests can take fun selfies and share them through text messages and social media.
• A rooftop seating area with views of historic downtown Le Mars.
• Handicap accessibility throughout the building.
• Event center space that can hold up to 200 guests. The space can be rented for parties, meetings and other gatherings.
• The Wells Family Theater, where a short film plays multiple times each hour to tell the story of how Wells and Le Mars came together.
• An engaging Heritage Wall filled with vintage pictures and more to document the unique history of Wells.
• An updated gift shop filled with ice cream-inspired items.
• More space to house all these attractions. The remodeled visitor center/ice cream parlor includes 19,000 square feet, up from 12,000 square feet.

Guests can visit the revamped Wells Visitors Center and Ice Cream Parlor in downtown Le Mars. Members of the Wells team have been welcoming the media and the public to the remodeled facility. Shown here (left to right) are Shannon Rodenburg, Visitor Center marketing and tourism manager; Brenda Phelan, associate manager of food operations: Jean Ann Weiland, associate manager of team operations; Adam Baumgartner, vice president of retail sales; and Brett Susemihl, manager of the Visitor Center and Ice Cream Parlor.
Above all, the parlor reflects Wells’ mission to bring joy to everyday life because of the love of ice cream. “We’re building on a unique family legacy,” Baumgartner said. “We want to put a smile on the face of ice cream lovers for years to come.”
Discover the history of the sweetest place on Earth
All this drives economic development in rural Iowa. Wells employs nearly 3,000 people and produces 150 million gallons of ice cream each year.
“Wells gets all of its fresh dairy from within 75 miles of our production facilities in Le Mars,” said Shannon Rodenburg, marketing and tourism manager for the Wells Visitor Center and Ice Cream Parlor. “Wells collects and processes more than 20 tankers of milk each day, 365 days a year.”
It all began on Oct. 24, 1913, when Fred H. Wells signed a contract with Ray Bowers, a dairy farmer in Le Mars, for “one grey horse, one milk wagon, two barn cans, three 20-quart jars, 60 half-pint jars and the good will of the milk business he has in the city of Le Mars, Iowa,” all for $250. (That’s roughly $6,400 today.) The original contract granted Wells the milk distribution route and guaranteed a source of raw milk from Bower’s herd of 15 cows.
Around 1925, Wells and his sons began manufacturing ice cream in Le Mars. As the popularity of their ice cream grew, they quickly branched out and began distributing their frozen confections in Remsen and Alton, Iowa, the following year. By 1927, Wells and his brother, Harry C. Wells, began a partnership to distribute ice cream in Sioux City.
A big change occurred, however, in 1928, when Fairmont Ice Cream purchased the ice cream distribution system in Sioux City from the Wells brothers, along with the right to use the Wells name. That could have been the end of the ice cream business for Wells, but it wasn’t.
Seven years later, in 1935, the Wells brothers decided to again sell ice cream in Sioux City. No longer able to use the name “Wells,” the brothers decided to run a “Name That Ice Cream” contest in the Sioux City Journal. A Sioux City man, George Vanden Brink, won the $25 cash prize for submitting the winning entry, “Blue Bunny,” after noticing how much his son enjoyed the blue bunnies in a department store window at Easter time. Vanden Brink, who was an illustrator by trade, also created the first Blue Bunny logo, which appeared on Blue Bunny packaging for nearly 70 years.

The revamped Wells Visitors Center and Ice Cream Parlor offers an expanded ice cream menu with more novelties, extreme shakes and desserts, including the Monster Peanut Butter Cup Sundae.
What started as Blue Bunny Ice Cream® has grown to include multiple brands and licensed products today. The company makes nearly 1,000 different products, Baumgartner said.
In fact, there is more ice cream made in Le Mars than in any one location on Earth, making Le Mars the Ice Cream Capital of the World—a title the community has held since Iowa’s state legislature made it official in 1994.
Bringing the ice cream story to life
From a single delivery wagon to the world’s largest family-owned and managed ice cream producer, Wells’ 100+ years in the industry is a pretty sweet story. The company has set its sights on becoming the leading ice cream manufacturer in the nation.
Giving Wells’ ice cream parlor/event center a facelift is part of a bigger goal to make Le Mars a destination, Baumgartner said. “Iowa has a lot of great things to offer. This is a place you have to see. You’ll love it.”
Want more?
Thanks for stopping by. I invite you to read more of my blog posts if you value intriguing Iowa stories and history, along with Iowa food, agriculture updates, recipes and tips to make you a better communicator.
If you’re hungry for more stories of Iowa history, including more stories of Wells and Blue Bunny, check out my top-selling “Culinary History of Iowa: Sweet Corn, Pork Tenderloins, Maid-Rites and More” book from The History Press. Also take a look at my latest book, “Dallas County,” and my Calhoun County” book from Arcadia Publishing. Both are filled with vintage photos and compelling stories that showcase he history of small-town and rural Iowa. Order your signed copies today! Iowa postcards are available in my online store, too.
If you like what you see and want to be notified when I post new stories, be sure to click on the “subscribe to blog updates/newsletter” button at the top of this page, or click here. Feel free to share this with friends and colleagues who might be interested, too.
Also, if you or someone you know could use my writing services (I’m not only Iowa’s storyteller, but a professionally-trained journalist with 20 years of experience), let’s talk. I work with businesses and organizations within Iowa and across the country to unleash the power of great storytelling to define their brand and connect with their audience through clear, compelling blog posts, articles, news releases, feature stories, newsletter articles, social media, video scripts, and photography. Learn more at www.darcymaulsby.com, or e-mail me at yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Let’s stay in touch. I’m at darcy@darcymaulsby.com, and yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Talk to you soon!
Darcy

In the past year, Wells has invested $3 million in upgrades and expansions for the Wells Visitors Center and Ice Cream Parlor in downtown Le Mars. Guests can enjoy their ice cream in the retro-styled dining area or new movie theater upstairs.
@Copyright 2019 Darcy Maulsby & Co. Blog posts may only be reprinted with permission from Darcy Maulsby.

Why We Should Never Stop Asking Why
Ever been asked to speak at career day at the local middle school? If you haven’t, trust me when I say it’s an eye-opening, slightly nerve-wracking experience.
I volunteered with the Calhoun County Farm Bureau to speak at Ag Day on March 26 at the Manson Northwest Webster Middle School about my travels to Vietnam and South Korea a few years ago with the Iowa Corn Growers’ I-LEAD leadership group.
Then I headed west to Sac City on March 29 to share my “True Confessions of an Ag Journalist” program during the Sac County Farm Bureau’s I Am Ag career day, where professionals from veterinarians to bankers spoke about the pros and cons of their careers.
Throughout the day, each speaker is assigned a classroom, and we share our story 12 times in 25-minute segments. I always go home from these events exhausted, but I hope I added value for the students and helped spark their desire to keep learning.
What always amazes me is how different the response is from the sixth graders to the eighth graders. The sixth graders are excited to learn and have no fear of asking questions. In fact, many of them are quick to raise their hands to ask questions and share comments.
Everything changes when the eighth graders walk in the room. Many of these kids want to show you just how bored they are. Some convey clearly through their body language and comments that don’t want to be stuck in a classroom. Their eyes tell you in no uncertain terms that they’re just waiting to defy anyone who dares to challenge them to think and learn.
Undaunted, I tell every group of students I work with that one of the keys to being a successful writer/storyteller/journalist (or any leader, for that matter) is to be like the little kid who never stopped asking why. Always nurture your sense of wonder and curiosity. Not only is that how we learn, but it makes life more fun!
Why do we lose the why?
This experience made me wonder why so many people lose their desire to ask questions.
A Newsweek story, “The Creativity Crisis,” described the signs of declining creativity among our school children. The article noted that preschool kids ask their parents an average of 100 questions a day. WOW! By middle school, however, kids basically stop asking questions.
It is also around this time student motivation and engagement drop like a rock. Why? Our educational system tends to reward students for having the answer, not for asking good questions. Ask a question, and you risk looking ignorant.
Yet knowing how to ask the right questions in the right way is essential to career success, more enjoyable conversations, stronger interpersonal relationships and effective leadership. I can only tell compelling, clear stories for my clients and through my books when I ask the right questions.
 Questions I use
Questions I use
I often work from a tried-and-true, proven set of open-ended questions that encourage sources to open up so we can go beyond the superficial and dig deeper to get to the good stuff—the defining moments, the setbacks, and the dreams that add life and vitality to any story.
Here are some of my key questions
1. What’s some of the best business advice—or advice for life—you’ve ever received?
2. What’s your motivation (for your work, or your life)?
3. What three things inspire you? (These can be people, books, movies, art, places, etc.)
4. What three words describe you?
5. What three words describe your company?
6. What’s something odd/interesting/unique about you? (This fun fact should not be so personal you would only share it with a therapist, but also not so safe it will bore us!)
7. How did you get started in the business you’re in?
8. Think back to when you first hit adulthood. What did you think your life would be like? What was your plan A? Are you still with Plan A, or did you move on to Plan B?
9. What obstacles did you overcome to get where you are today?
10. What’s a specific story of success in your business that drives you to do what you do? (A customer that really affected you, a person you were able to help, an accomplishment you were able to achieve?)
11. What do you like about your work?
12. What helpful lessons did you learn from previous jobs that you apply to your current role?
13. What’s the weirdest thing that’s ever happened to you at work?
14. What’s the best thing that ever happened to you/you witnessed at work?
15. How did your company get started?
16. What excites you about the future?
You can modify these questions (or create your own) and put them to work in your business, your home or your classroom. Please tell me how it goes, too. Don’t be surprised if I ask you why you think these questions work. I love to learn and hope you do to, too!
No matter what, never stop asking “why” about the world around you. We need more critical thinkers. Also remember the words of playwright George Bernard Shaw: “Some men see things as they are, and ask why. I dream of things that never were, and ask why not.”
Want more?
Thanks for stopping by. I invite you to read more of my blog posts if you value intriguing Iowa stories and history, along with Iowa food, agriculture updates, recipes and tips to make you a better communicator.
If you like what you see and want to be notified when I post new stories, be sure to click on the “subscribe to blog updates/newsletter” button at the top of this page, or click here. Feel free to share this with friends and colleagues who might be interested, too.
Also, if you or someone you know could use my writing services (I’m not only Iowa’s storyteller, but a professionally-trained journalist with 20 years of experience), let’s talk. I work with businesses and organizations within Iowa and across the country to unleash the power of great storytelling to define their brand and connect with their audience through clear, compelling blog posts, articles, news releases, feature stories, newsletter articles, social media, video scripts, and photography. Learn more at www.darcymaulsby.com, or e-mail me at yettergirl@yahoo.com.
If you’re hungry for more stories of Iowa history, check out my top-selling “Culinary History of Iowa: Sweet Corn, Pork Tenderloins, Maid-Rites and More” book from The History Press. Also take a look at my latest book, “Dallas County,” and my Calhoun County” book from Arcadia Publishing. Both are filled with vintage photos and compelling stories that showcase he history of small-town and rural Iowa. Order your signed copies today! Iowa postcards are available in my online store, too.
Let’s stay in touch. I’m at darcy@darcymaulsby.com, and yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Talk to you soon!
Darcy
@Copyright 2019 Darcy Maulsby & Co. Blog posts may only be reprinted with permission from Darcy Maulsby.

Senator Grassley on Farming: Any Society is Only Nine Meals Away From a Revolution
When people ask about my latest book project and I tell them about Iowa’s Ag History, I get two reactions: either a blank stare, or “Oh cool!” When I reached out to Iowa Senator Charles Grassley, a farmer, to share a few comments for the book, I received more than an enthusiastic response.
I got an incredible interview from a senator who was willing to offer a significant portion of his time to share his insights into the importance of history, agriculture and rural Iowa’s role in the modern global economy. Read on to see why Sen. Grassley says, “I like to remind policymakers that any society is only nine meals away from a revolution.”
When did your family start farming in Iowa?
I am the second generation farmer in my family, following in the footsteps of my father Louis Grassley. His dad emigrated from Germany and died when my dad was just seven years old. At around age 18, my dad started working as a hired hand for the Heitland family on a farm in Hardin County. A few years later, he rented some land near New Hartford in Butler County. In 1927, he and my mother Ruth purchased their own parcel of land.
After graduating from high school, I worked in factories, attended college and farmed with my dad. In 1958, while running for the Iowa legislature and working towards my doctorate at the University of Iowa, I started farming my own piece of the family farm. When my dad passed away in 1960, I rented his 80 acres and about five years later, purchased 120 acres on my own.
When I started out, I grew a bit of everything like most farmers at the time. I grew corn, soybeans, oats and alfalfa and raised sheep, cattle and hogs. My son Robin Grassley, a third-generation farmer, and I continue farming 750 acres together. He rents and owns other farmland along with my grandson Pat Grassley, who is a fourth-generation family farmer.
Barbara and I raised our five children together on our farm near New Hartford, and we enjoy passing on our agrarian heritage and celebrate family gatherings here with our grandchildren and great-grandchildren.
In politics as in farming, a solid understanding of the past is vital to understand current issues. From your unique viewpoint as a senator and a farmer, what’s your take about why it’s important to be well-versed in history–and what are the perils of not knowing history?
As a lifelong farmer who also has worked for six decades representing Iowans in state and federal government, I wear my rural roots as a badge of honor and believe it’s important for farmers to have a seat at the policy-making tables. Farmers take the long view of things, and maybe that’s why they don’t forget important lessons from history.
Only two percent of the American population shoulders the responsibility for growing enough food to feed the U.S. population. Our agrarian-based heritage has experienced rapid transformation in the last generation. Fewer Americans, even in Iowa, have a direct link to living or working on a farm. And most likely due to the affordable abundance of food, not enough people appreciate that food security is directly tied to national security. Food security extends beyond national sovereignty. American agriculture – and the farmers, workers and businesses along the supply chain – anchors the U.S. economy and increasingly strengthens U.S. energy independence, as well.
From a historical perspective, there are two rules of thumb I use to explain how important food security is to maintain peace and prosperity in society. As Emperor of France in the early 19th century, Napoleon Bonaparte reportedly said “to be effective, an army relies on good and plentiful food.” In other words, an army marches on its stomach. Food security ensures a nation can feed its military, whose men and women in uniform are deployed to protect and defend a nation’s sovereignty, at home and abroad. I also like to remind policymakers that any society is only nine meals away from a revolution.
Political leaders who embrace the misguided notion that socialism is the answer to peace and prosperity are either grossly misinformed or willfully ignorant about the peril of leaders who promise to fix “inequality” with government control. Just look at the economic crisis in Venezuela, once one of the most prosperous nations in the Western Hemisphere. The poverty and humanitarian crisis falls squarely in the hands of the nation’s authoritarian regime and its ideologically driven policies. History teaches us that when government suppresses freedom and liberty, the people’s path towards peace and prosperity is replaced with food and medicine shortages, hyperinflation, power outages and even more economic and social inequality.
History teaches us other important lessons. Namely, how not to repeat the mistakes of the past. Don’t forget, the overly harsh tariffs in the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1932 shut down world trade, led to a worldwide economic depression and foretold a world war that killed tens of millions of people.
Another important lesson I keep in mind at the policy-making tables is the 1980s farm crisis. The loss of thousands of family farms was a heart-wrenching loss for so many families and long-time neighbors across Iowa. It stole a sense of vitality from small towns and rural communities. It arguably steered away a generation of beginning farmers from following in the footsteps of their parents and grandparents. The farm crisis invigorated my advocacy on behalf of young and beginning farmers, including my work to push for robust enforcement of anti-trust laws and oversight of mergers and competition in the agriculture industry. Previously, I’ve introduced legislation that would have amended the Packers and Stockyards Act to make it illegal for a packer to own, feed or control livestock intended for slaughter. I’ll keep my oversight hat on to protect the integrity of the marketplace so that independent producers have a fair shake at a fair price for their commodities.
I also led efforts to enact and make permanent Chapter 12 in the federal bankruptcy code. This unique chapter is designed to help farmers and ranchers who have fallen on hard times to survive bankruptcy and restructure their debts without losing their livelihood. Most recently, I secured an update to Chapter 12 to fix court rulings that undermined congressional intent. Previously, the IRS muscled its way to the front of the creditor’s line to scoop up capital gains taxes and potentially block a farmer’s reorganization plans. Farmers shouldn’t be penalized for being asset-rich and cash-poor. When they need to reorganize debts to hold on to their livelihoods, my reforms ensure they aren’t going to be slapped with a big tax bill and lose the ability to continue farming.
Another way I advocate for family farmers at the policy-making tables is my longstanding efforts to restore fiscal integrity to the farm safety net. In our free market society, farmers ought to be able to decide how large or small they want their operation to be. However, the farm safety net shouldn’t be manipulated for operations to grow at taxpayer expense. It’s very important to uphold the credibility and strengthen the public trust in the farm safety net, as well. That’s why I will continue my efforts to attach reasonable payment limits so that off-site managers, including nieces, nephews, cousins and other family members who aren’t actually contributing to the operation of the farm, are prevented from cashing in on farm payments.
In 2019, I launched my 39th consecutive year holding meetings in each of Iowa’s 99 counties. I keep in close touch with Iowans and count on this dialogue to make representative government work. I also apply the lessons of history to inform my work on making better policies and fixing laws that create unintended consequences. As chairman of the Senate Finance Committee, which has oversight and legislative jurisdiction over international trade, I’m currently working to reform a 1962 federal law that delegated authority to the executive branch. Specifically, Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act authorizes the president to impose tariffs on selected imports if the chief executive determines those imports pose a threat to our national security.
This law was enacted with good intentions and for good reason. However, history has shown that reforms are necessary in order to give Congress a role in the process. In my view, Congress delegated too much authority to the executive branch at the expense of the people’s branch. American agriculture too often shoulders the burden of retaliatory action from our trade partners. It’s another example of why I always check the rear-view mirror to ensure the road ahead paves the way for prosperity and opportunity for family farmers and all those who earn their livelihoods and enjoy their way of life in Rural America.
What are some of the biggest changes in Iowa agriculture you’ve seen and experienced in your lifetime?
Technology and innovation have revolutionized farming as we know it. Mechanization allows an individual farmer to dramatically improve productivity and harvest bin-busting yields grown from disease-resistant seeds, for example. At the same time, farmers are able to conserve resources and save money using no-till, cover crops and precision agriculture. As a first-generation farmer, my dad used a team of horses when he started farming. Like many family farmers, the genetic code of fiscal discipline, conservation and ingrained work ethic was handed down to me from my parents’ experience carving out a living from the land. In my case, the Grassley household and farming operation was influenced by the Great Depression, to conserve resources and stretch every penny.
To this day, I carry a lifelong code of conservatism with me as a farmer and lawmaker. Although innovation – including WiFi-enabled farms and climate-controlled tractor cabs — hasn’t shortened the work day for most farmers, it’s certainly transformed productivity and changed the way we market our crops and livestock. When I started farming on my own in the 1950s, the average corn yield in Iowa was about 45 bushels/acre. Today Iowa farmers yield an average of 202 bushels/acre. This productivity helps feed and fuel a growing world population with affordable, wholesome food and renewable energy. So increased productivity has been revolutionary.
Another significant change is farmers are affected by worldwide market forces. That means a farmer in the 21st century must be able to survive not just the whims of Mother Nature, but also the winds of geo-political negotiations and foreign policy that impact exports and a farmer’s bottom line.
Ag literacy should be part of education, in my opinion, for any Iowa student. In your opinion, how does a basic understanding of agriculture benefit all Iowans, both rural and urban?
No matter what policy we may be debating in Congress, I often find the best way to sum up the debate boils down to this: Washington is an island surrounded by reality. As a farmer-lawmaker on the Senate Agriculture Committee, I bring a dirt-underneath-my-fingernails perspective to the policy-making tables. I take pride serving as a champion for rural America to advocate for our nation’s food producers and farm families. With only two percent of the population growing food for the rest of the nation, it’s more important than ever to educate consumers about where their food comes from. In fact, I often suggest that many Americans are under the mistaken impression that food grows in grocery stores, restaurants or take-out containers. I’m glad to see more and more farmers’ markets becoming a vital part of local communities. It’s good for the local economy and community vitality and fosters better awareness that food does not grow on the grocery store shelf.
With a global population expected to reach nearly 10 billion people by 2050, the importance of agriculture research and education is vital for human civilization. Iowa’s deeply rooted agrarian heritage continues to lead the way with excellent opportunities to foster ag literacy, food, plant and animal science and entrepreneurship. Iowa boasts a vibrant network of FFA organizations across the state. What’s more, Iowa’s native son Norman Borlaug paved an agricultural revolution credited with saving a billion people from starvation. The Father of the Green Revolution was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1970 and Iowa celebrates his legacy with a statue in the Rotunda of the U.S. Capitol.
Iowa is also home to the World Food Prize. Since 1987 the World Food Prize Foundation has celebrated the achievements of individuals inspired by the legacy of Dr. Borlaug. Each year it awards individuals whose contributions have improved the global food supply, from plant, animal and soil science to technology and nutrition and rural development. For three decades, it has brought thousands of people from around the world to Des Moines in October to talk about food security in a symposium known as the Borlaug Dialogue.
Anything else you’d like to add about the importance of knowing history in general and the history of agriculture in Iowa in particular?
Iowans may know I love history. In today’s polarized world of identity politics, it’s important more than ever to strengthen civic education in America’s classrooms. Our youngest members of society need to understand the perils of communism, fascism and socialism. Regimes inspired by utopian socialist principles do not eradicate hunger or poverty, they extinguish peace and prosperity at the expense of individual freedom and liberty.
Despite the regional, ideological and partisan differences that divide Americans, we share a common humanity and fundamental thread of human existence. We all need to eat to survive. And I’m proud to be among the generations of Iowa farmers who have answered the vocational calling to put food on family tables. As a steward of the soil and U.S. Senator for Iowa, I am honored to serve as a voice for agriculture and rural America.
Want more?
Thanks for stopping by. I invite you to read more of my blog posts if you value intriguing Iowa stories and history, along with Iowa food, agriculture updates, recipes and tips to make you a better communicator.
If you like what you see and want to be notified when I post new stories, be sure to click on the “subscribe to blog updates/newsletter” button at the top of this page, or click here. Feel free to share this with friends and colleagues who might be interested, too.
Also, if you or someone you know could use my writing services (I’m not only Iowa’s storyteller, but a professionally-trained journalist with 20 years of experience), let’s talk. I work with businesses and organizations within Iowa and across the country to unleash the power of great storytelling to define their brand and connect with their audience through clear, compelling blog posts, articles, news releases, feature stories, newsletter articles, social media, video scripts, and photography. Learn more at www.darcymaulsby.com, or e-mail me at yettergirl@yahoo.com.
If you’re hungry for more stories of Iowa history, check out my top-selling “Culinary History of Iowa: Sweet Corn, Pork Tenderloins, Maid-Rites and More” book from The History Press. Also take a look at my latest book, “Dallas County,” and my Calhoun County” book from Arcadia Publishing. Both are filled with vintage photos and compelling stories that showcase he history of small-town and rural Iowa. Order your signed copies today! Iowa postcards are available in my online store, too.
Let’s stay in touch. I’m at darcy@darcymaulsby.com, and yettergirl@yahoo.com.
Talk to you soon!
Darcy
@Copyright 2019 Darcy Maulsby & Co. Blog posts may only be reprinted with permission from Darcy Maulsby.






